Article access: https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/mBio.02220-21
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has caused huge deaths and economic losses worldwide in the current pandemic. A traditional Chinese medicine formula (TCM) has played an important role in the treatment of COVID-19 in China. However, the mechanism of TCM action is still unclear. Academician GAO Fu’s group identified leupeptin, a metabolite produced by plant-symbiotic actinomyces (PSA), which showed antiviral activity in both cell culture and enzyme assays. Moreover, leupeptin found in the Qing-Fei-Pai-Du (QFPD) decoction was confirmed by both high-performance liquid chromatography fingerprinting and high-resolution mass spectrometry. These results suggest that leupeptin likely contributes to the antiviral activity of the QFPD decoction against SARS-CoV-2. This result provided important insight into further studies of the PSA metabolite and medicinal plant ecosystem for future TCM modernization research. The research group thus propose that plants, microbiome, and microbial metabolites form an ecosystem for the effective components of TCM herbs.
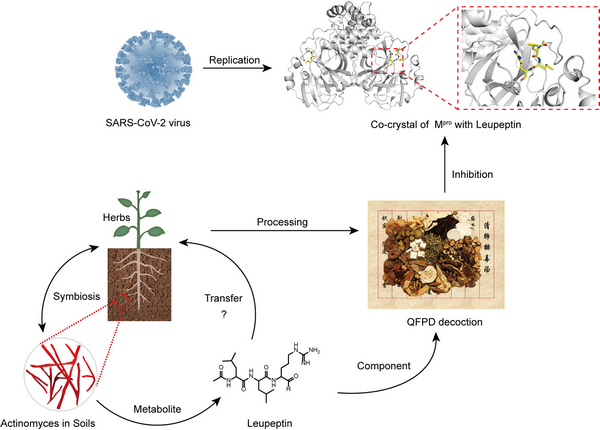
Fig 1 Plant-symbiotic actinomyces and antiviral activity ecology of microbial bioactive compounds, such as leupeptin, contribute to the antiviral activity of the QFPD decoction against SARS-CoV-2 Mpro.